Security concepts
- Principal – user, device or system that performs an action
- Authentication – establishing that a principal’s credentials are valid
- Authorization – deciding if a principal is allowed to access a resource
- Authority – Permission or credential enabling access
- Secured Resource – Resource that is being secured
Architecture
SecurityContextHolder – The SecurityContextHolder is where Spring Security stores the details of who is authenticated.
SecurityContext – is obtained from the SecurityContextHolder and contains the Authentication of the currently authenticated user.
Authentication – Can be the input to AuthenticationManager to provide the credentials a user has provided to authenticate or the current user from the SecurityContext.
GrantedAuthority – An authority that is granted to the principal on the Authentication (i.e. roles, scopes, etc.)
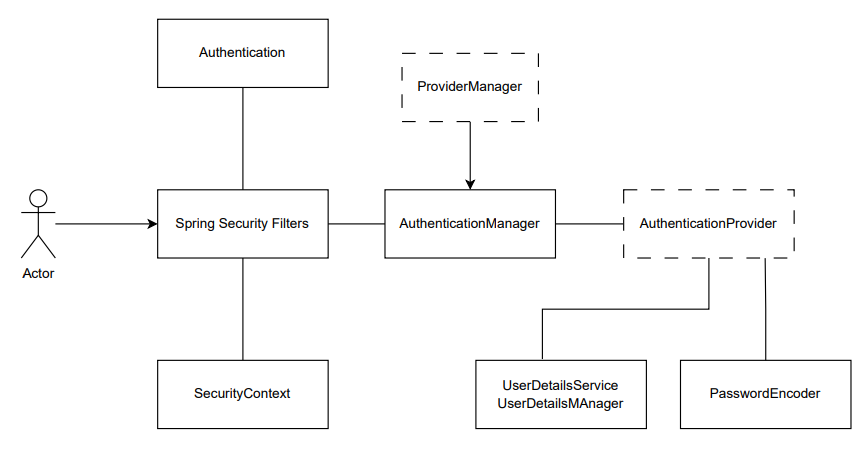
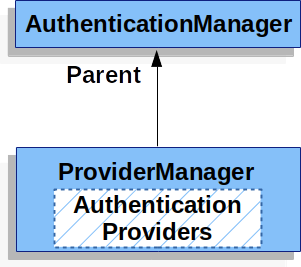
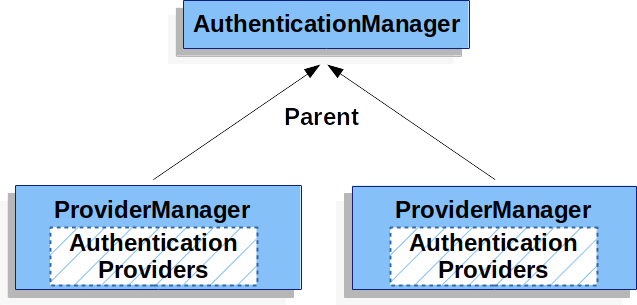
AuthenticationManager – the API that defines how Spring Security’s Filters perform authentication.
ProviderManager – the most common implementation of AuthenticationManager.
AuthenticationProvider – used by ProviderManager to perform a specific type of authentication.
Request Credentials with AuthenticationEntryPoint – used for requesting credentials from a client (i.e. redirecting to a log in page, sending a WWW-Authenticate response, etc.)
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter – a base Filter used for authentication. This also gives a good idea of the high level flow of authentication and how pieces work together.1
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/reference/servlet/authentication/architecture.html
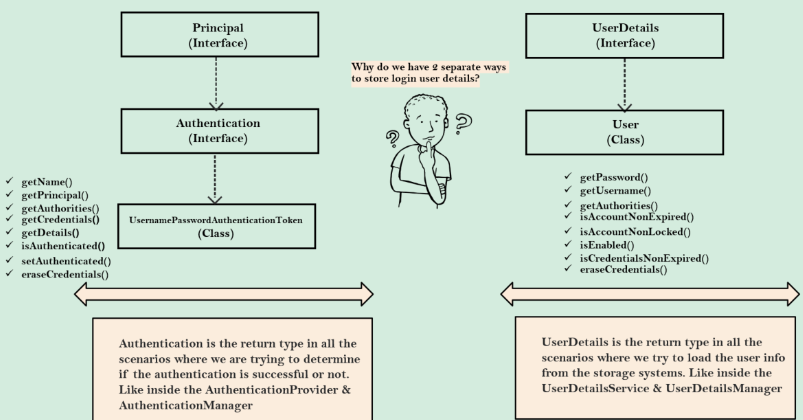
Authentication
Authentication is the core object that stores authentication details, it will be stored in thread local local security managed by SecurityContextHolder. Authentication extends Principal.

Security Flow
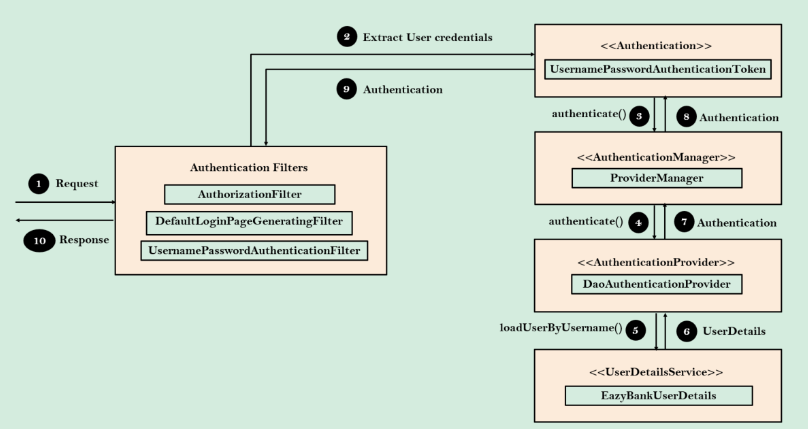
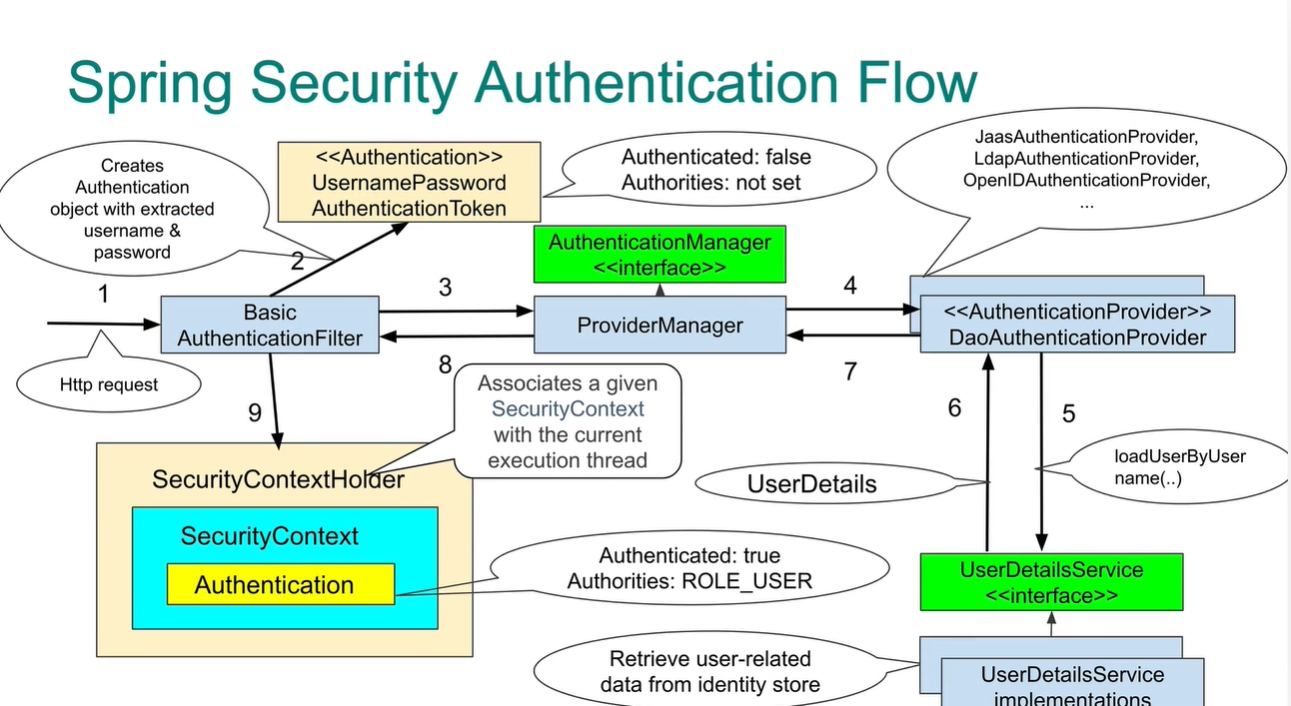
DaoAuthenticationProvider
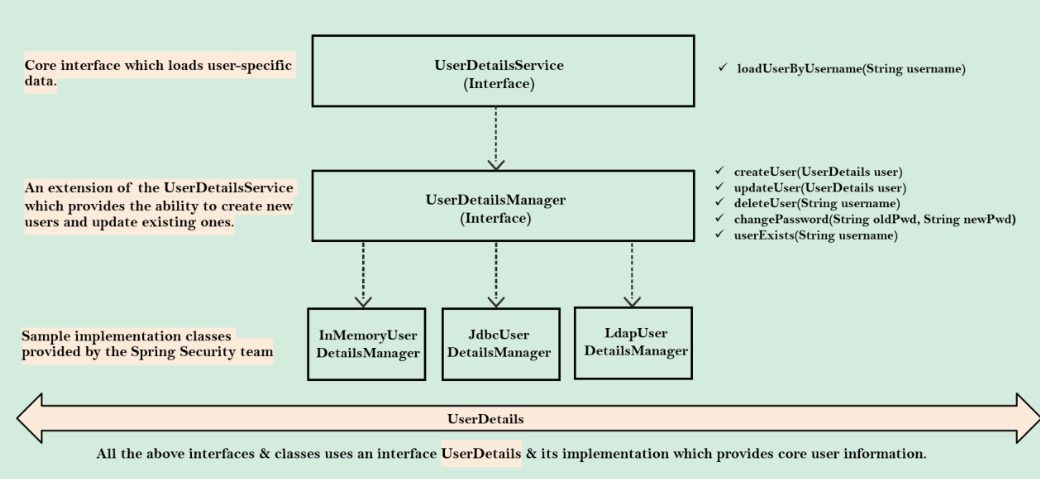
DaoAuthenticationProvider is an AuthenticationProvider implementation that uses a UserDetailsService and PasswordEncoder to authenticate a username and password.
UserDetailsService (loadUserByUsername) is used by DaoAuthenticationProvider for retrieving a username, a password, and other attributes for authenticating with a username and password. Spring Security provides in-memory, JDBC, and caching implementations of UserDetailsService.
Password Storage
Each of the supported mechanisms for reading a username and password can use any of the supported storage mechanisms:
- Simple Storage with In-Memory Authentication (InMemoryUserDetailsManager)
- Relational Databases with JDBC Authentication (JdbcUserDetailsManager )
- LDAP storage with LDAP Authentication (LdapUserDetailsManager)