
Spring Boot lets you externalize your configuration so that you can work with the same application code in different environments. You can use a variety of external configuration sources including Java properties files, YAML files, environment variables, and command-line arguments.
Property values can be injected directly into your beans by using the @Value annotation, accessed through Spring’s Environment abstraction, or be bound to structured objects through @ConfigurationProperties.
Spring Boot uses a very particular PropertySource order that is designed to allow sensible overriding of values. Later property sources can override the values defined in earlier ones. Sources are considered in the following order:
- Default properties (specified by setting
SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties). @PropertySourceannotations on your@Configurationclasses. Please note that such property sources are not added to theEnvironmentuntil the application context is being refreshed. This is too late to configure certain properties such aslogging.*andspring.main.*which are read before refresh begins.- Config data (such as
application.propertiesfiles). - A
RandomValuePropertySourcethat has properties only inrandom.*. - OS environment variables.
- Java System properties (
System.getProperties()). - JNDI attributes from
java:comp/env. ServletContextinit parameters.ServletConfiginit parameters.- Properties from
SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON(inline JSON embedded in an environment variable or system property). - Command line arguments.
propertiesattribute on your tests. Available on@SpringBootTestand the test annotations for testing a particular slice of your application.@DynamicPropertySourceannotations in your tests.@TestPropertySourceannotations on your tests.- Devtools global settings properties in the
$HOME/.config/spring-bootdirectory when devtools is active.
Config data files are considered in the following order:
- Application properties packaged inside your jar (
application.propertiesand YAML variants). - Profile-specific application properties packaged inside your jar (
application-{profile}.propertiesand YAML variants). - Application properties outside of your packaged jar (
application.propertiesand YAML variants). - Profile-specific application properties outside of your packaged jar (
application-{profile}.propertiesand YAML variants).
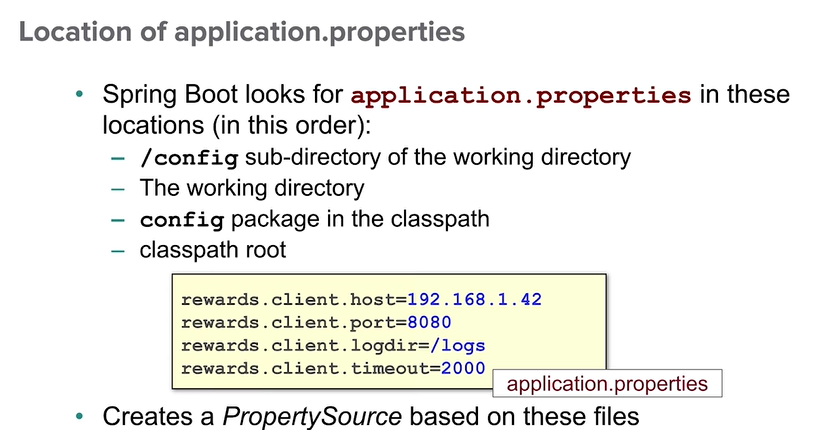
Spring Boot will automatically find and load application.properties and application.yaml files from the following locations when your application starts:
- From the classpath
- The classpath root
- The classpath
/configpackage
- From the current directory
- The current directory
- The
config/subdirectory in the current directory