Microservices are small, loosely coupled, distributed services, allow to decompose applications in easy-to-manage components with narrowly defined responsibilities.
A microservices architecture would have the following characteristics:
- Application logic is broken down into small-grained components.
- Each component has a small domain of responsibility and it’s deployed completely independently of one another.
- Communication is based on few basic principles and used lightweight communication protocols like HTTP and JSON.
- Independent of language or technology.
- Built by small development team with well-defined areas of responsibility.
Some of the principles that must be taken in account when designing a microservices architecture:
Right-sized – ensure microservices are properly sized and that one microservice doesn’t take on too much responsibility.
Location transparent – how to abstract the application from physical details of machines and services.
Resilient – protect microservice consumers and overall integrity of your application by routing failing services and ensuring a fail-fast approach.
Repeatable – ensure that every new instance of service is brought up having the same configuration and code as the other currently running the service.
Scalable – How to scale applications quickly and minimize dependencies between services.
Microservices Patterns
There are common challenges for any microservices architecture that consist in several types of patterns:
- Core development
- Routing
- Client resiliency
- Security
- Logging and tracing
- Build and deployment
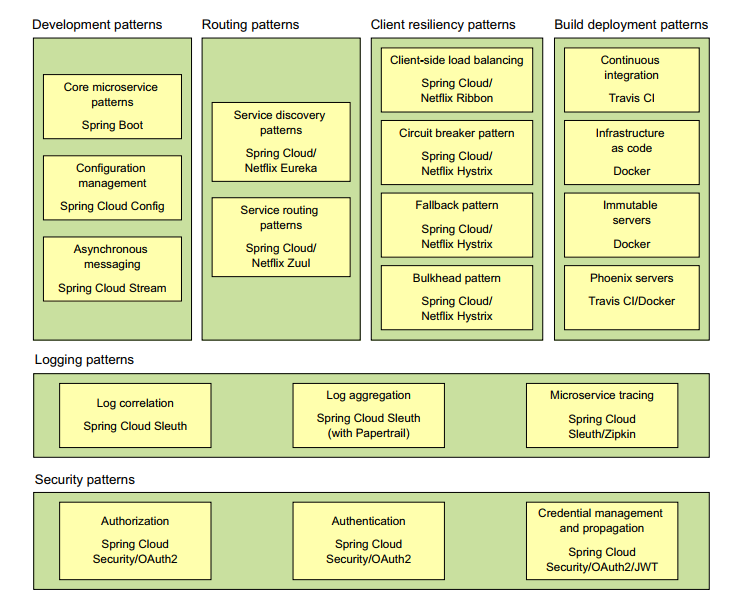
(credits: Spring microservices in action)