Concepts
Principles for Rest:
- expose resources through url’s
- resources support limited set of operations
- clients can request an particular representation
- representations can link to others resources
- should be stateless
Crud operations
The components of the Request and Response are:
Request
- Method (also called Verb)
- URI (also called Endpoint)
- Body
Response
- Status Code
- Body
If you want to go into more depth around Request and Response methods, check out the HTTP standard.
The power of REST lies in the way it references a Resource, and what the Request and Response look like for each CRUD operation. Let’s take a look at what our API will look like when we’re done with this course:
- For CREATE: use HTTP method POST.
- For READ: use HTTP method GET.
- For UPDATE: use HTTP method PUT.
- For DELETE: use HTTP method DELETE.

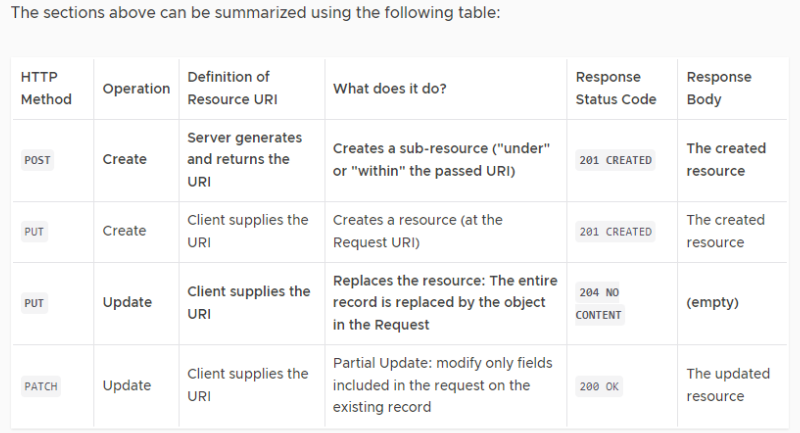
Post vs Put

Idempotency
Idempotent: PUT, DELETE, GET, DELETE
Non-idempotent: POST, PATCH